Posted
on November 17,
2019 by beyondnuclearinternational
Citizen
scientists are uncovering risks that governments would rather cover up
By
Cindy Folkers
When
reactors exploded and melted down at the Fukushima nuclear power complex in
March 2011, they launched radioactivity from their ruined cores into the
unprotected environment. Some of this toxic radioactivity was in the form
of hot particles (radioactive microparticles) that congealed and became
airborne by attaching to dusts and traveling great distances.
However,
the Fukushima disaster is only the most recent example of atomic power and
nuclear weapons sites creating and spreading these microparticles. Prior
occurrences include various U.S. weapons sites and the ruined Chernobyl
reactor. While government and industry cover up this hazard, community
volunteer citizen science efforts – collaborations between scientists and
community volunteers – are tracking the problem to raise awareness of its
tremendous danger in Japan and across the globe.
After
the Fukushima nuclear disaster began, one highly radioactive specimen, a
particle small enough to inhale or ingest, was found in a private home where it
should not have been, hundreds of miles from its source, in a vacuum cleaner
bag containing simple house dust.
This
“high activity radioactively-hot dust
particle” came from a house in Nagoya, Japan – after it had traveled 270
miles from Fukushima. The only radioactive particle found in the home’s vacuum
cleaner bag, it was an unimaginably minuscule part of the ruined radioactive
core material from Fukushima – many times smaller than the width of a human
hair. We know it came from Fukushima because it contained cesium-134, meaning
that the particle came from a recent release, and we know it is a piece of core
material specifically because it was so radioactive that it could not have come
from any other material.
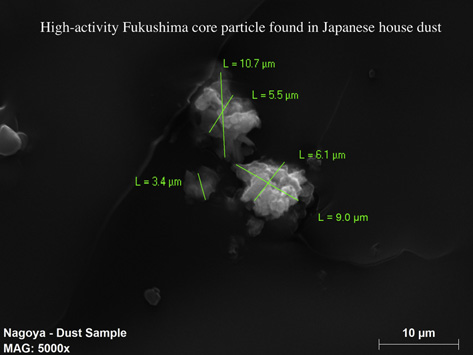
(Image courtesy of Arnie Gundersen/Fairewinds)
Most
of the particle’s radioactivity came from cesium-134 and cesium-137. By the
time it was collected, some of the particle’s radioactivity, mostly from
iodine-131, had already decayed. Named “corium” by scientists, it was still thousands of times more
radioactive (5,200,000,000,000,000 disintegrations per second per
kilogram — that’s 5.2 quadrillion more than the average activity (26,000
disintegrations per second per kilogram) found in dust and soil samples
collected through community volunteer efforts from across Japan — with a focus
on areas around Fukushima — since the 2011 nuclear disaster began. By way of
comparison, in the U.S., average soil and dust activity is thousands of times
lower.
Due
to privacy concerns, we are not permitted to know the identities of the Nagoya
residents who participated in the dust sampling collection and in whose home
the particle was found. Nor do we know how many people lived in the home; if
there were children or babies present; or pets; or pregnant women. And we will
never know if there were any other radioactive microparticles in the home that
did not make it into that vacuum cleaner bag.
We
do not know how the particle got there. No one in the home (nor the vacuum
cleaner) had any connection to the Fukushima reactors or the exclusion zone.
Was the particle transported by a car tire into their city? On someone’s shoes?
Did it fly in through a window after being lofted by air currents? Did it
arrive by a combination of forces? We do not know if other particles like this
travelled just as far in all directions, or who may have taken a breath at just
the wrong moment, so that a similar microparticle might be lodged in their
lungs.
We
do know the residents in Nagoya were notified about the particle’s presence,
and that if it had been inhaled or ingested, it could have proven lethal over
time. This corium particle would have destroyed tissue near it, potentially
threatening the function of any organ that tissue was part of. But the
particle’s additional danger would come from what it didn’t destroy – that is
tissue that is damaged but survives and can go on to mutate into cancer or
non-cancer diseases.
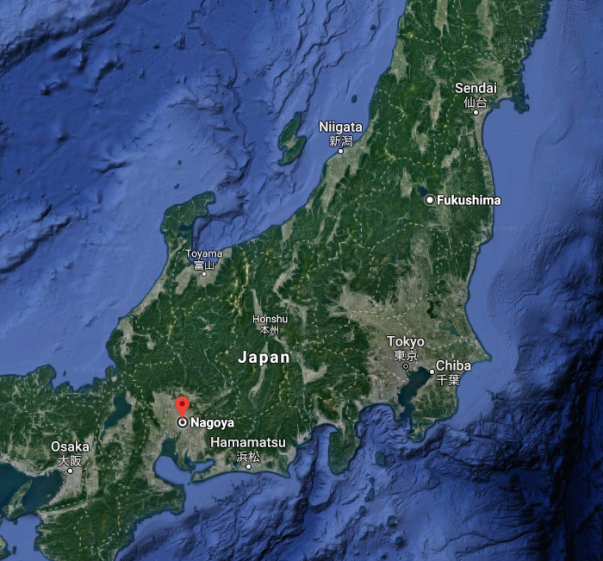
A map showing the distance between Nagoya,
where the radioactive “hot particle” was found, and Fukushima.
We
also know that had scientists and citizens not worked together to collect samples,
we would never have known a microparticle of corium existed at all at a
distance so far away from the Fukushima meltdowns. If the presence of this
particle – and its potential for inhalation – had gone unnoticed, any
calculations of the doses to residents of this home would have been
significantly underestimated. And while the Nagoya particle may simply be an
outlier, it shows how inaccurate radiation risk assessment has turned out to
be. All of these microparticles, even ones less
radioactive, may pose significant health
risks inside the body that are currently uncalculated.
Citizen
and scientists collaborations show us that radioactive microparticles are a
worldwide problem. Yet action by public health advocates and government
officials has been slow to nonexistent in recognizing this danger, much less
working to protect people against exposure from it. Detecting radioactive
microparticles is extremely difficult, in part because detecting them and
proving their danger requires specialized techniques and equipment. But this is
no excuse for governments to ignore the problem altogether as they continue to
do. When experts tell us what our risks are from radiation exposure, risks from
these microparticles remain unaccounted for in every country in the world.
Speculation swirls around these
particles and whether the rapid-onset cancers occurring in Japan are possibly
due to their presence.
Radioactive
particles across the globe
Collections
of various samples (home air filters, vehicle engine intake filters, soils,
samples of dust from vacuum cleaner bags) have revealed radioactive
microparticles from Fukushima made it as far as Seattle,
WA and Portland, OR in the U.S.,and to the Western coast of Canada.
Not
surprisingly, microparticles in Japan were much more radioactive than those
that made their way to the U.S. and contained more varied radioisotopes, thus
posing a much greater health risk. In the case of some filters in Japan,
contamination was high enough to be classified as “radioactive waste.”
In
addition to catastrophic releases from nuclear power facilities, these
particles come from atomic detonations, other nuclear industry processes such
as mining and atomic fuel fabrication, and nuclear facility releases of
radioactivity, as well as leaking atomic waste dumps. Nuclear workers, First
Nations Tribes, and local residents have submitted samples for testing around
such facilities. Particles have been detected in the environment and
in house dusts in communities around weapons facilities in Los Alamos, NM;
Hanford, WA; and Rocky Flats, CO. Thorium, plutonium, and uranium from nuclear
facilities were found “outside of radiation
protection zones,” including workplaces, workers’ homes and cars. “Given the
small respirable size of these radioactive microparticles, they are a potential
source of internal exposure from inhalation or ingestion,” according to Dr.
Marco Kaltofen of Worcester Polytechnic Institute.
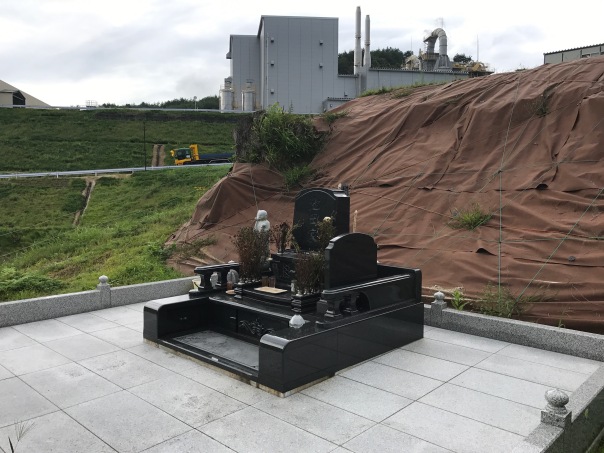

A single-family, private burial site, whose
backdrop is covered bags of radioactively contaminated soil. (Photo courtesy of
Arnie Gundersen/Fairewinds)
In
some cases, radioactive particle releases can be higher from nuclear power
catastrophes than disasters at atomic bomb facilities. In 1986, Chernobyl
also released radioactive particles
that still contaminate the environment today. . Forest fires are spreading them further. Current
community volunteer citizen science efforts are underway in the environs of the
Santa Susana Field Laboratory (SSFL) – a former reactor test site adjacent to
Simi Valley, CA – and the site of several unanticipated and unmonitored nuclear
releases, a meltdown, and the November 2018 Woolsey forest fire.
Similar
work is being carried out in Pike County, OH, host to a uranium enrichment
facility for military and civilian nuclear reactors that has spread radioactive
contamination to a nearby middle school, the grounds of which have now
been quarantined. The U.S. Department of
Energy hid the school contamination for two years, prompting public outrage and
calls for health investigations into the high incidence of local childhood
disease.
Ignoring
danger to human health, environment
The
U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) currently has an existing 10-mile
emergency planning radius around commercial nuclear power reactors, a zone the
NRC does not place around other nuclear facilities. This 10-mile zone is not
large enough to account for exposures that often occur well outside of it.
While
the NRC is aware of the radioactive
microparticle threat, its dose models fail to provide the
extensive, detailed calculations required to actually protect anyone working at
or living near these sites. Since radioactive microparticles remain a threat
for generations after a catastrophe begins, the NRC should account for
continuing exposure to communities and their people for the decades or centuries
it takes for such materials to be safe for human or animal exposure.
The
author wishes to thank Arnie and Maggie Gundersen at Fairewinds Energy Education for technical and
editorial input. Cindy Folkers is the radiation and health specialist at Beyond Nuclear.
Headline
photo: “3S0578” by Billy and Lynn is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.